virtual storage area network (VSAN)
What is a virtual storage area network (VSAN)?
A virtual storage area network (VSAN) is a logical partition in a physical storage area network (SAN). VSANs enable traffic to be isolated within specific portions of a SAN, so if a problem occurs in one logical partition, it can be handled with minimal disruption to the rest of the network.
Businesses rely on the use of multiple, isolated VSANs to make a storage system easier to configure and scale out. Subscribers can be added or relocated without needing to change the physical layout.
How VSAN works
A VSAN appliance enables unused storage capacity on virtual servers to be pooled and accessed by virtual servers as needed. A VSAN can pool local storage resources from a cluster of servers within a data center into a single shared storage pool.
This is achieved by taking multiple, disparate physical data storage devices -- such as solid-state drives or hard disk drives -- and virtualizing them to form a single data resource. That resource appears to servers as a traditional SAN or network-attached storage (NAS) device, without using dedicated SAN or NAS storage devices.
A VSAN appliance is often a software program that runs on a virtual machine, but some storage hardware vendors have incorporated VSAN appliances into their firmware. Depending on the vendor, a virtual SAN appliance might also be called a software-defined storage appliance.
VSAN vendors and features
The acronym for a virtual storage area network is spelled differently by the vendors that offer storage virtualization products with different features. When spelled with all capital letters, the acronym is often associated with Cisco Systems and is talked about in conjunction with zoning, which splits a physical SAN into multiple, isolated subnetworks. When spelled with a lowercase V, the acronym is usually associated with VMware and Hyper-V features that allow available hard disk drive storage to be pooled from across clustered hosts.
Today, most storage software or hardware vendors offer some form of VSAN for their own or other vendors' storage and server hardware. A number of vendors offer software-only packages that let users assemble their own virtualized storage environments using off-the-shelf servers and storage devices.
VSAN platforms help achieve hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) by combining a business's compute and storage resources into a consolidated storage solution. The HCI approach enables effective management that's needed to protect critical infrastructure workloads from disruption or failure.
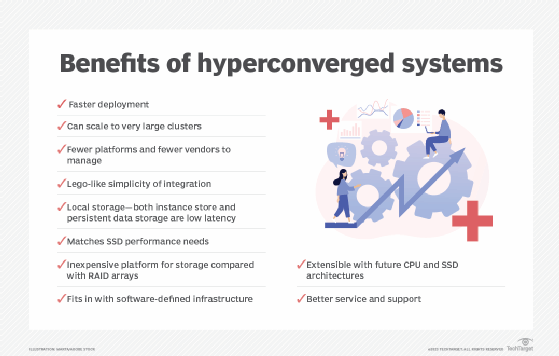
Benefits of virtual storage area networks
The following are among the benefits that a VSAN can provide:
- Nondisruptive data migration. A VSAN enables adopters to migrate data between storage resources easily and without downtime.
- Better information lifecycle management. Storage virtualization makes it easier to ensure data is stored on the appropriate device. This puts frequently accessed data on high-performance storage and less frequently accessed data on lower-performing, less expensive storage resources.
- Improved manageability. Storage management can become difficult when storage resources involve several vendors or even different models from the same vendor. The virtualized view of storage resources that a VSAN enables makes storage configuration, provisioning and management of storage easier.
- Overall simplicity. Compared to the alternatives, a VSAN is easy to provision and manage because it's embedded within the hypervisor. That enables faster installation and configuration.
- Reduced total cost of ownership (TCO). A VSAN can be deployed on inexpensive x86 servers and with generic storage devices. This eliminates the need for upfront investments in expensive physical storage arrays and reduces TCO.
Virtual storage area network use cases
A VSAN may prove useful for various real-world use cases, such as storage automation, edge computing and adding new security layers to IT infrastructure. Some use case examples include the following:
- Server virtualization. Virtualization converts local, physical storage devices into virtual storage to consolidate unused storage capacity so it can be managed more efficiently.
- Cloud automation. VSANs often have features and functions that handle cloud storage automation.
- Demilitarized zones and test environments. Vendors provide demilitarized zones, also known as security zones, to further isolate internal infrastructure and applications. These also provide an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access.
- Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). VDI environments let administrators run apps on a host server in either an on-premises or a cloud data center. They can then deliver those apps over a network to end users' devices.
- Support edge computing sites. VSANs create shared storage environments that are useful for edge devices operating in remote locations and sometimes austere environments. If an edge server is disrupted, a VSAN can keep it running until the problem is addressed and remedied.
- Disaster recovery. VSANs provide advanced data security and recovery capabilities that can simplify disaster recovery. These include replication and snapshots, data protection, scalability, flexibility and high availability of critical applications and data.
Different approaches to data center storage are available to enterprises. Learn about each approach and its uses.