workflow automation
What is workflow automation?
Workflow automation is an approach to making the flow of tasks, documents and information across work-related activities perform independently in accordance with defined business rules. When implemented, this type of automation should be a straightforward process that is executed on a regular basis to improve everyday productivity.
Workflow is a series of activities needed to complete a task. Workflow automation shifts the performance of those activities from humans to a software program.
To automate a workflow, an organization first identifies the tasks that make up the job. It next creates the rules and logic that govern how those tasks should be done. Finally, it programs the software with the predefined business rules and logic.
The rules and logic are often a series of if-then statements that act like instructions telling the program what actions to take and how to move from one task to the next. The software uses those rules and logic to perform the series of tasks from start to finish, so that humans no longer have to handle the job.
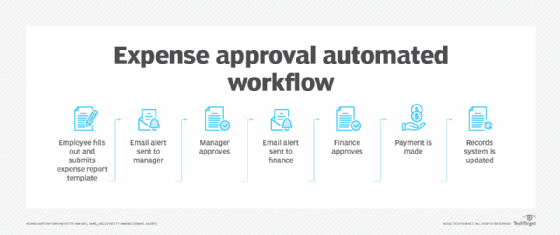
Who uses workflow automation?
All organizations have areas that could benefit from automating repetitive notifications, permissions and other basic tasks.
A 2021 report from automation software maker Zapier found that 94% of small and medium-sized business (SMB) workers surveyed said they perform repetitive, time-consuming tasks. The report also noted that 90% of knowledge workers found that automation improved their jobs and 66% said automation has made them more productive.
In an enterprise, every department can use a workflow automation system -- including finance, human resources (HR), marketing, operations and sales. It is typically used to automate jobs that involve repetitive tasks and don't require significant levels of intellectual decision-making.
Organizations generally seek to automate workflows for the following reasons:
- increase efficiency
- reduce errors
- boost productivity
- speed up processes
They also implement workflow automation so employees can spend less time on tedious, low-value tasks. This approach gives workers more time to focus on jobs that require human intellect.
Many workflow automation software packages on the market have low-code, drag-and-drop features that let workers themselves automate manual processes that are part of their workplace responsibilities. Some workflow automation tools include artificial intelligence capabilities, which can handle tasks that require a certain level of decision-making.
Workflow automation is most often used in the following circumstances:
- A task is repetitive.
- A task needs to be achieved accurately without human error.
- A series of simple tasks can be made more efficient.
When used in such cases, workflow automation enables an organization to streamline its business processes and increase workplace efficiency and productivity.
Importance of workflow automation
Workflows should be automated whenever possible for numerous reasons, including to achieve faster operations and to increase the efficiency and accuracy of automated tasks.
Workflow automation is important for other reasons as well, including the following:
- High-value tasks. By relieving workers of mundane, low-value tasks, automation frees them to work on higher-value, nonautomated tasks that only humans can handle.
- Savings. Increased productivity generates cost savings.
- Visibility. The workflow mapping that's used to program automation software creates visibility into the processes being automated. That gives an organization a top-down view of its workflows that can help it remove outdated or redundant tasks that drain time and resources.
- Communication. That increased visibility in turn can improve employee and interdepartmental communication and coordination, further enhancing efficiency and eliminating bottlenecks.
- Customer service advantages. By automating responses to customer inquiries, organizations can improve customer service and customer satisfaction. Of the nearly 300 executives surveyed for the 2021 Global Customer Success Survey from software maker SmartKarrot, 84% said automation is important or extremely important for their customer service operations.
- Product quality. With human error eliminated, overall product quality improves.
- Performance tracking. By digitalizing the tasks within a workflow, automation can track performance of the workflow from end to end. This enables an organization to easily review how well its business operates.
These attributes are important because they boost an organization's ability to compete in the digital era. The Zapier report spoke to this point, noting that 88% of SMBs surveyed said automation enables their companies to compete with larger entities.
Benefits of workflow automation in business processes
Benefits of workflow automation include the following:
- reduced workflow cycles;
- less need for manual labor and handling of products;
- better adherence to compliance rules and regulations;
- more visibility into workflow tasks;
- increased ability to identify and remove operational bottlenecks;
- optimized customer experience, satisfaction and service;
- improved employee satisfaction, resulting from the elimination of repetitive tasks;
- real-time insights provided by workflow analysis tools such as dashboards and key performance indicators (KPIs);
- opportunities to engage in the continual improvement of workflows due to the increased operational insights;
- better workload management due to the increased operational insights;
- better internal and external communications and coordination;
- more accountability for who is responsible for what because each step in the business workflow is clearly assigned;
- more employee time for high-value tasks;
- increased productivity;
- lower operational costs;
- higher workflow accuracy as automation removes the potential for human error;
- improved ability to scale because workflow automation can be adjusted as demand goes up and down; and
- more efficient task management, with the inclusion of dashboards, calendars and other tools that can be made available through workflow automation software tools.
Workflow automation examples
Below are four examples of tasks that workflow automation can handle:
- organizing document approval and signing;
- moving employees, partners and customers through processes;
- facilitating invoicing and other accounting- and sales-related processes; and
- responding to customer inquiries and requests.
Uses of workflow automation
Organizations across all industries can benefit from workflow automation. Moreover, they can use this technology in various departments and niche areas such as supporting DevOps workflows within the IT department.
The following examples illustrate the applicability of workflow automation in industries and departments:
Healthcare. Medical providers use workflow automation to generate staff work schedules and on-call rotations. Providers also use these tools to support patient admission and discharge and to transfer patients' electronic health records. In each of these areas, workflow automation lets healthcare workers focus on more important work, such as direct patient care.
Legal. Whether in the legal industry itself or in the legal function within an enterprise, workflow automation is used to automate billing, input new client information, submit and track contract reviews and manage case deadlines.
Information technology. IT departments use automation to support DevOps teams and other groups. They use it to automate the orchestration of the software development pipeline, data monitoring, data collection, testing code development, service requests, new account setup and the deployment of tests and code. For example, a DevOps group could automate the testing of a new e-commerce app.
Financial. Financial businesses and groups within an enterprise use workflow automation for data entry and account approval processes. In the enterprise, they also use it to automate tasks such as paid time off requests and salary adjustments.
Marketing. Workflow automation can help with various aspects of marketing automation, making tasks associated with brand management and campaigns happen automatically in a prescribed order.
Sales. These departments often automate the approval of proposals and quotes, the introduction of salespeople to leads generated through website interactions and the generation of a task list once a lead schedules a meeting with a sales rep.
Cybersecurity. Workflow automation speeds incident response, making the process more efficient.
Human resources. Automation facilitates various HR processes, such as time sheet approvals, onboarding and offboarding employees and managing personnel changes.
Operations. Workflow automation is used for a multitude of tasks, including compiling reports and assigning tasks.
Workflow automation steps
Implementing workflow automation software typically involves the following seven steps:
- Identify the processes that would make good candidates for automation, namely those made up of repetitive manual tasks. In doing this, prioritize the workflows that are most inefficient and prone to human error or ones that are expensive to do manually.
- Map out the process and design the workflow. This step requires an in-depth knowledge of business operations.
- Define the business goals. Organizations should articulate how implementing workflow automation can deliver on specific goals, whether those goals involve saving money, improving efficiency, reducing errors, boosting productivity or delivering another benefit typically associated with this technology.
- Research, choose and implement the workflow automation software. Organizations should pick software that has the features, functions and service-level agreements at the right price point to help them achieve their stated business goals.
- Train employees to use the workflow automation software, supporting the initiative with a solid change-management program.
- Establish KPI metrics and use them to measure success and adjust automated workflows to meet the goals.
- Drive continuous improvement by gathering employee feedback, which combined with the KPIs can improve the user experience and the overall workflow.
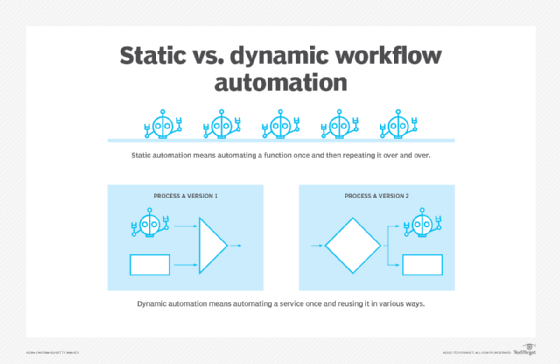
Dynamic vs. static workflows
Workflow automation can be either dynamic or static.
When automated workflow is static, there is no variance in the steps taken. They take place in a strict sequence, whether or not there are variables that could potentially affect the outcome.
When automated workflow is dynamic, software can use a schema template to determine at runtime what step should be taken next. A dynamic workflow paired with automation can promote agility.
Popular workflow automation software tools and apps
Demand for workflow automation is significant. Research firm MarketWatch estimated the value of the global workflow automation market to be $7 billion in 2021 and projects it will reach more than $16 billion by 2028.
Vendors in this space include IBM, Oracle and Xerox, as well as newer ones such as Appian and Pegasystems.
In addition to standalone workflow automation platforms, many vendors offer function-specific software that has workflow automation capabilities. For example, HubSpot includes workflow automation within its marketing, sales and customer service software.
Some enterprise platforms, such as customer relationship management systems, also have tools to automate workflows.
Many vendors market their workflow automation as low-code solutions. This means they do not require extensive understanding of programming to use. Instead, they have drag-and-drop features that let users automate workflows within their jobs with little or no need to involve IT professionals.
Any organization seeking to implement workflow automation must pay attention to the capabilities of the software it selects. It should be easy to use, cost-effective and capable of delivering on the organization's business goals.
Workflow automation software is usually distributed as a software as a service (SaaS) application. SaaS apps commonly include simple workflow tools aimed at SMBs.
Vendors offering workflow automation technology include the following:
- Catalytic has a no-code workflow automation platform for digitizing business operations.
- Flokzu is a cloud-based platform that provides workflow templates and icons to enable business users with no coding experience to automate workflows.
- IBM offers an automation platform with a modular set of integrated software components called Cloud Pak for Business Automation.
- Integrify has cloud-based low-code software for automating processes and streamlining workflows. It also offers a REST-based open API that enables users to integrate with other external databases and report data from different files, such as Excel and PDFs.
- Kissflow makes automation software with an intuitive interface that lets users create automated workflows with preinstalled business process management (BPM)
- Microsoft offers Power Automate (previously Microsoft Flow), enabling users to automate workflows and BPM.
- Nintex features workflow automation and process intelligence in its software, which also requires little to no coding.
- Pipefy enables users to centralize and streamline workflows by automating tasks on a low-code/no-code platform.
- ProcessMaker is a web-based, open source workflow automation and business process automation tool.
- SmartSuite provides collaborative work management software with a drag-and-drop interface so users can set up even complex automations.
- Zapier makes the automation process easier by having users pick a trigger and then an action.
Workflow engine vs. business rules engine
Organizations can use both a workflow engine and a business rules engine (BRE), but they are not the same thing.
- A workflow engine is a software application or tool that helps users automate a series of tasks that make up a workflow -- usually within a specific time frame. The software application that is used in workflow automation can be referred to as a workflow engine. The workflow engine helps an organization save time and effort in moving a process along.
- A BRE is used to make autonomous decisions based on a set of rules. BREs operate on a set of conditions in software, which executes an app's code if specific criteria are met. In short, BREs set criteria for how software should behave in different states.
A workflow engine is operated with the goal of workflow management. A BRE, on the other hand, doesn't have any input on orchestrating tasks. A BRE is more of a guideline for how software will make specific decisions given certain circumstances. Nontechnical users without much coding knowledge can use a BRE to change their software's behavior based on defined business requirements.
Workflow automation vs. robotic process automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) technology copies how people use software for high-volume, repeatable tasks. RPA technology creates bots that then handle workflow tasks such as data entry, calculations and copying.
Conceptually, RPA is similar to workflow automation. The difference is RPA is useful for automating individual discrete tasks, while workflow automation is useful for automating a series of tasks.

Both workflow automation and RPA rely on technology to automate tasks, but workflow automation places more emphasis on communication between disparate elements of the workflow. For example, in a supply chain process, workflow automation software might be used to make sure the right person is notified at the right time about what work has to be next for each step of the process. RPA would only focus on one task within the process.
Learn more about RPA in our comprehensive guide.





